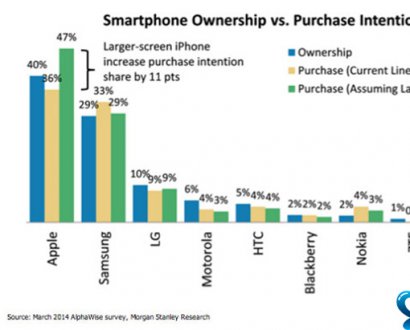
危险的毒蜘蛛。(A)来自南美洲的黑寡妇(Latrodectus),背面观。黑色的腹部有对比鲜明的白色和红色的人字形斑纹。(A)一种北美黑寡妇(Latrodectus mactans),腹部腹侧有典型的(红色)沙漏斑纹。(C)一只棕色隐居蜘蛛的肖像(Loxosceles);请注意六只眼睛和悬挂在螯肢之间的毒液滴(箭头)。(D)南美洲一种颇具攻击性的蜘蛛Ctenid Phoneutria fera的肖像。(Photos b–d: Rast.)
Without any treatment the symptoms will last for about 5 days, and a complete recovery may take weeks. About 80 years ago, lethality was 5% in the United States (Thorp and Woodson, 1945), but since 1970 it is less than 1% (Zahl, 1971). The best treatment against a bite from a black widow is a combination of calcium gluconate with opioids and benzodiazepines plus an antivenom (McCrone and Netzloff, 1965; R. F. Clark, 2001). Calcium causes the pain to subside quickly, and the antidote binds to the toxin. The patient feels relieved within 10–20 minutes and will recover within a few days (Isbister and Gray, 2003).The venom (BWSV) is a neurotoxin that affects the neuromuscular endplates (fig. 4.30b) but also affects synapses in the central nervous system. The synaptic vesicles become completely depleted, causing a permanent blockage of the synapse (Clark et al., 1972; Griffiths and Smyth, 1973; Tzeng and Siekevitz, 1978;Wanke et al., 1986). One component of the poison (a-latrotoxin) binds to a presynaptic receptor of cholinergic synapses (Meldolesi et al., 1986). This is in contrast to toxins in orb-web spiders, which act on synapses that use glutamate as neurotrans- mitter (Kawai et al., 1982; Michaelis et al., 1984). Over the past years a number of spider toxins have been used extensively in neurobiological research because they block specific ion channels (e.g., for Ca2+) of the cell membrane (Adams et al., 1989; Jackson and Parks, 1989).
如果不进行任何治疗,这些症状将持续大约5天,完全恢复可能需要数周时间。大约80年前,美国的致死率是5%(Thorp and Woodson,1945),但自1970年以来,这一数字不到1%(Zahl,1971)。针对黑寡妇咬伤的最佳治疗方法是葡萄糖酸钙与阿片类药物结合、以及苯二氮卓类药物和抗蛇毒血清的结合(McCrone and Netzloff, 1965; R. F. Clark, 2001)。钙会使疼痛迅速消退,解毒剂会与毒素结合。患者在10-20分钟内感觉缓解,并将在几天内恢复(伊斯比斯特和格雷,2003年)。蛛毒是一种神经毒素,影响神经肌肉终板(fiG.4.30b),但也影响中枢神经系统中的突触。突触小泡变得完全耗尽,导致突触的永久性阻塞((Clark et al., 1972; Griffiths and Smyth, 1973; Tzeng and Siekevitz, 1978;Wanke et al., 1986)。毒素的一种成分(a-乳头状毒素)与胆碱能突触的突触前受体结合(Meldolesi等人,1986年)。这与圆网蜘蛛中的毒素形成对比,后者作用于使用谷氨酸作为神经传递因子的突触上(Kawai et al., 1982; Michaelis et al., 1984)。在过去的几年中,许多蜘蛛毒素被广泛用于神经生物学研究,因为它们阻断细胞膜的特异性离子通道(例如,钙离子通道) (Adams et al., 1989; Jackson and Parks, 1989)。
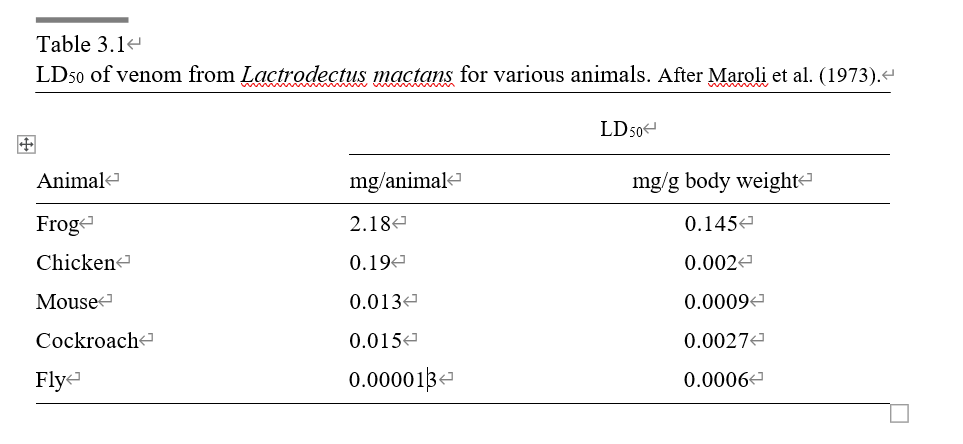
The lethal dose 50 (LD50) is usually given as a measure for the toxicity of a given substance. This term refers to the dosage of venom that will kill 50% of injected experimental animals. For the venom of Latrodectus mactans, the LD50 for a mouse is 0.0009 mg/g body weight. As can be seen in table 3.1, however, susceptibility to the venom varies greatly among different animals (Maroli et al., 1973).
致死剂量50(LD50)通常用来衡量特定物质的毒性。这个术语指的是毒液的剂量,可以杀死50%注射毒液的实验动物。对美国毒蛛Latrodectus mactans的毒液来说,小鼠的LD_(50)为0.0009毫克/克体重。然而,如表3.1所示,不同动物对毒液的敏感性差异很大(Maroli等人,1973年)。
上一篇:科学网期刊编辑该让作者推荐审稿人吗? 下一篇:科学网Secondary aperture模型开发助力制备高性能G